杰享是迈杰转化医学微信公众号新推出的专栏,作为精准诊断整体解决方案的领导者,我们在这里会以文献解读的方式,分享精准医学领域关于生物标志物、伴随诊断等主题的最新进展。
背景介绍
肿瘤淋巴结转移(Tumor Node Metastasis,TNM)分期仍然是结直肠癌患者预后分层的金标准,临床基于TNM分期结果选择对应的治疗方法。大部分II期结直肠癌患者在外科手术切除后,不进行辅助治疗的情况下可实现长期的无疾病生存(Disease Free Survival,DFS),但是约20%的患者会出现疾病进展并死亡,另外一些III期患者比某些II期患者的预后更好,说明现有的TNM分期在预后分层方面存在一定的缺陷。尽管对TNM指南进行了修订,例如将pT stage II细分为三类,有助于病理学家进一步细化评估患者肿瘤进展风险,但是预后分层结果仍然是高度主观的。
除了TNM分期,Tumor buds (TBs)也可用于结直肠癌患者的预后评估。TBs是指在肿瘤的侵入性边缘区域(Invasive Margin,IM)散布的小的、分化差的细胞簇(1-4个肿瘤细胞),与结直肠癌的不良预后相关。 TNM分期和TBs都只关注肿瘤细胞,但是越来越多的研究表明,肿瘤微环境(Tumor Microenvironment,TME)中的宿主免疫细胞浸润在肿瘤进展中起着至关重要的作用。特别是在大肠癌中,开创性研究表明CD3+、CD8+ T细胞浸润是预测患者生存的独立预后因素。因此免疫细胞和TBs之间的相互作用,可能预测肿瘤转移潜力。过往的研究表明,不仅可以通过自动化定量分析TME中的CD3+、CD8+ T细胞,从而替代主观性大的人工分析,同样,也可以通过自动图像分析来进行TBs分析。尽管免疫细胞肿瘤浸润程度和TBs的自动化定量分析均与患者的预后有关,但是没有同时研究过两种标志物之间的空间关系及其预后价值。
因此,Ines P. Nearchou等在American Association for Cancer Research上发表了文章《Automated Analysis of Lymphocytic Infiltration, Tumor Budding, and Their Spatial Relationship Improves Prognostic Accuracy in Colorectal Cancer》,使用多重免疫组织化学技术,在同一张切片上同时检测多个生物标志物,并基于业内领先的图像分析软件HALO,建立了淋巴细胞浸润程度、TBs在肿瘤中的空间关系自动化定量分析方法,并提高了结直肠癌预后分析的准确性及标准化程度。
文献快读
文章中通过建立基于HALO Next Generation Image Analysis Software的自动化分析流程,同时定量分析淋巴细胞浸润程度、肿瘤TBs密度及两者之间的空间关系,结合来自三个研究队列的II期结直肠癌患者临床数据,实现更准确的结直肠癌预后分析。
一、淋巴细胞浸润分析(Lymphocytic Infiltration Analysis)
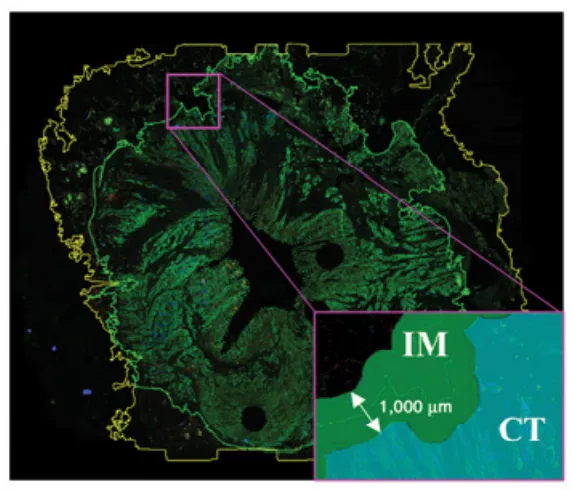
如图1所示,HALO软件可自动识别全组织区域(Full Tissue Area,Yellow Line)、肿瘤侵袭边缘(Invasive Front,Green Line),肿瘤侵袭区域(Invasive Margin,IM)包含肿瘤侵袭边缘内外延伸500 μm的区域,肿瘤核心区(Core Area of Tumor,CT)不包含肿瘤侵袭边缘内500 μm之内的区域:
图1. Full tissue area (yellow line) and invasive front (green line)are outlined; pancytokeratin (PanCK), CD3+, and CD8+ cells annotated in green,yellow, and red, respectively; IM region is highlighted in green and the tumor core region in blue (CT)
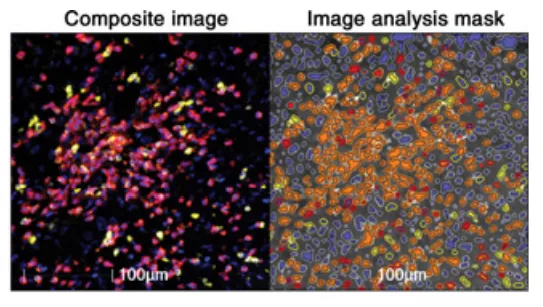
如图2所示,同时自动分析CT、IM内的CD3+、CD8+ T细胞浸润程度,通过计算T细胞密度(cells/mm 2)来评估预后价值:
图2. Detection and classification of lymphocyte cell type (CD3+ cells in yellow, CD8+ cells in red and their colocalization in orange mask)
二、肿瘤TBs分析(Tumor Budding Analysis)
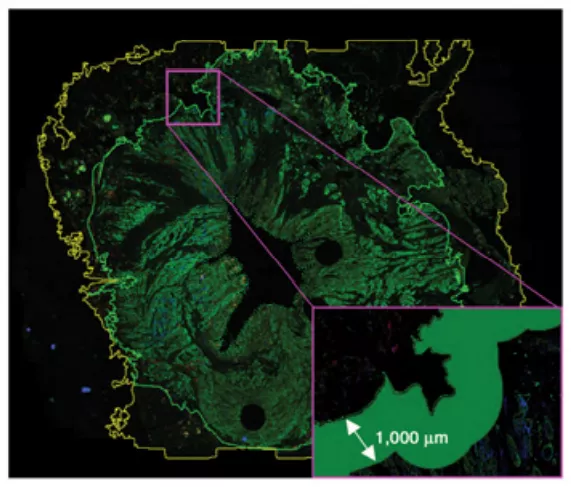
如图3所示,可自动分析IM内的TBs密度(TBs/mm2 ),进一步评估其预后价值:
图3. Full tissue area (yellow line) and invasive front (green line)are outlined, PanCK, CD3+, and CD8+ cells annotated in green, yellow, and red,respectively; area of TB quantification is highlighted in green
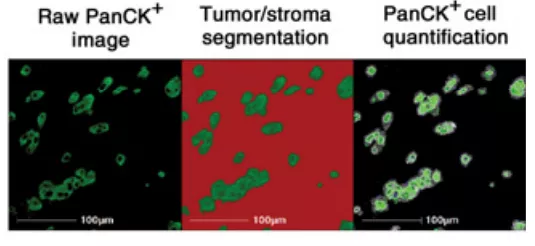
如图4所示,通过自动分析细胞角蛋白(Pancytokeratin,PanCK),可将肿瘤细胞与基质细胞区分开:
图4. Tumor to stroma segmentation and PanCK cell quantification within the tumor areas
三、淋巴细胞和TBs空间关系分析(Spatial Analysis of Lymphocytes and TBs)
如图5所示,基于HALO软件,可自动分析CD3+、CD8+ T细胞及TBs之间的空间定位关系:
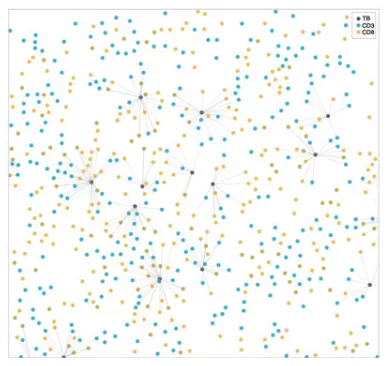
图5. Proximity analysis of lymphocytes to TBs. CD3+ cells are shown in blue, CD8+ cells in orange, and TBs in gray. Proximity line series is shown for lymphocytes within 50 mm of TBs
四、空间关系分析 (Statistical analysis)
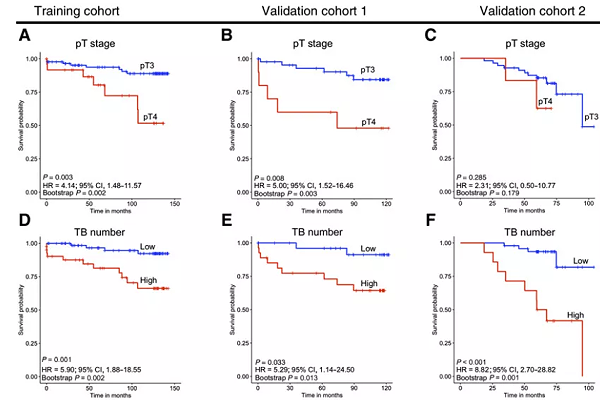
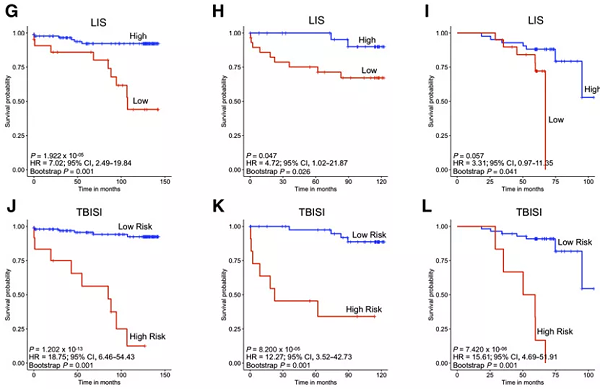
如图6所示,TBISI 指数(Tumor Bud Immuno Spatial Index) 同时分析淋巴细胞浸润、TBs,及两者空间关系,与传统的TNM分期及淋巴细胞浸润、TBs单指标分析,能更准确的提供II期结直肠癌预后分层结果:
图6. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis for pT stage, TB number,lymphocytic infiltration score (LIS), and TBISI for training cohort, validation cohort 1, and validation cohort 2
-
pT stage for training cohort
-
pT stage for validation cohort 1
-
pT stage for validation cohort 2
-
TB number for training cohort
-
TB number for validation cohort 1
-
TB number for validation cohort 2; High represents the group of patients with TB number above the optimal cutoff point (1104.0). Low represents the group of patients with TB number below the cutoff point
-
-
LIS for validation cohort 1
-
LIS for validation cohort 2. High LIS represents the group of patients with a LIS > 2, and low LIS represents the group of patients with a LIS ≤ 2
-
TBISI for training cohort
-
TBISI for validation cohort 1
-
TBISI for validation cohort 2. High risk represents the group of patients who have CD3+density in WTS and mean CD3+ CD8+ cell number within 0–50 mm of TBs below the cutoff point (389.6 cells/mm 2 and 4.1, respectively) and TB number above the cutoff point (1104.0). Low risk represents
all other patients
杰论
文章中使用多重免疫组化技术(Multiplex Immunohistochemistry,mIHC)来同时检测CD3+、CD8+ T淋巴细胞,以及使用PanCK区分肿瘤细胞及基质细胞,所有生物标志物的检测都在同一张切片上完成的。该技术可以克服常规IHC技术的局限性,仅需要一张组织切片,就可以同时检测多个标志物,并能研究组织细胞组成、细胞功能及细胞间相互作用。在肿瘤免疫治疗领域,这项技术在转化医学研究和临床实践中具有强大的应用潜力。
迈杰转化医学作为国内精准诊断整体解决方案的领导者,致力于解决精准医疗药物研发及患者用药痛点,围绕生物标志物研究、伴随诊断开发,建立了完善的核酸组学、蛋白组学、细胞组学技术平台。
在mIHC能力方面,整合了Leica Bond RX、PerkinElmerVectra3 System、HALO 三大平台。HALO是应用于数字病理图像分析的旗舰平台,兼容市面上所有主流数字病理扫描平台,提供全组织切片快速、准确的定量分析,对于HE、IHC、IF、ISH/FISH以及特殊染色的定量分析是理想的选择,可以适应任何图像分析应用。为助力药企加快药物研发进展,迈杰转化医学提供下列基于mIHC平台的服务:
参考文献
1. Ines
P. Nearchou , etal. Automated Analysis of Lymphocytic Infiltration, Tumor Budding,and Their Spatial Relationship Improves Prognostic Accuracy in Colorectal Cancer. Published Online First
March 7, 2019; DOI:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0377.